Perpetual Protocol 四:Exchange - 多市场管理的实现

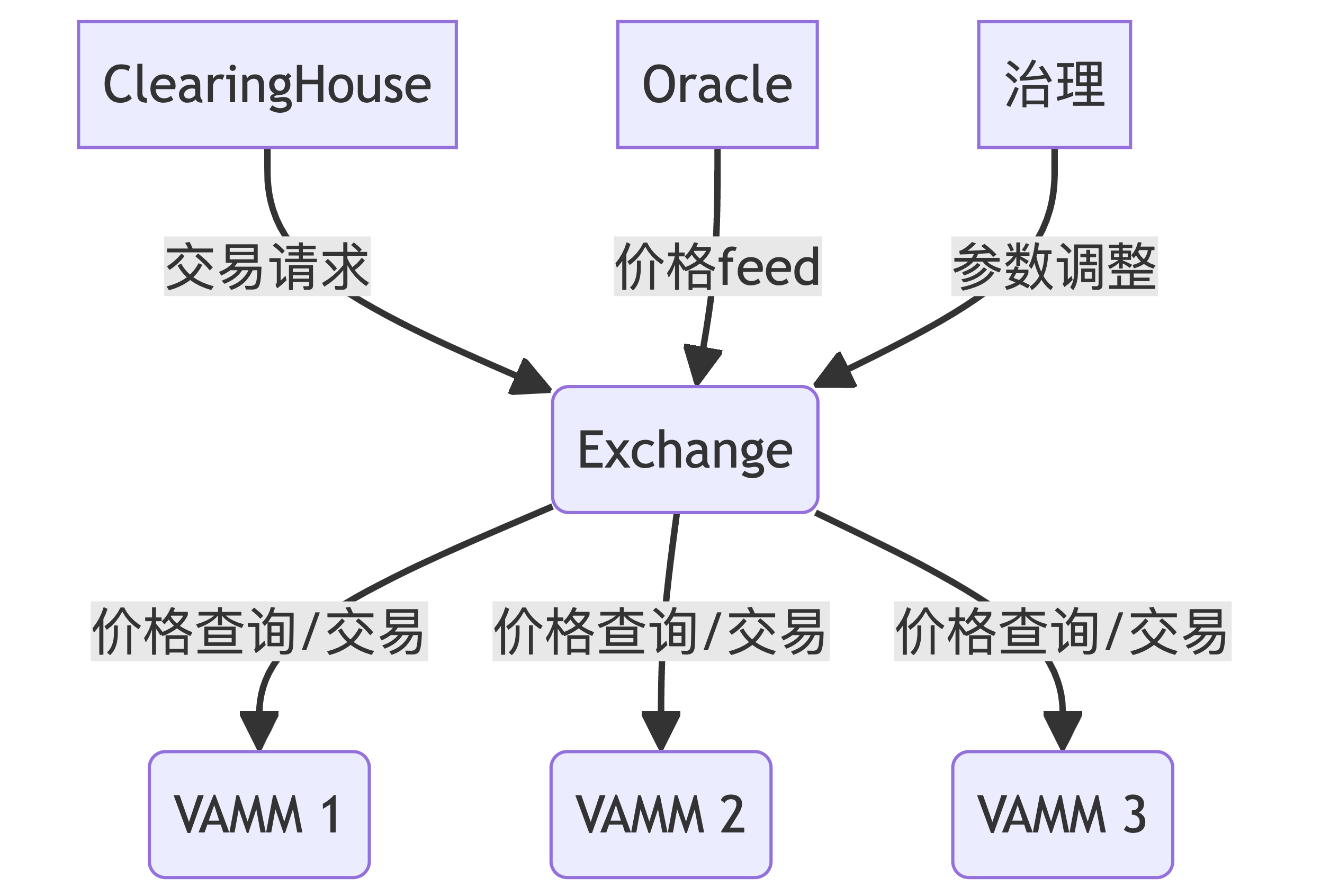
Exchange 合约在 Perpetual Protocol 中扮演着关键角色,负责管理多个交易市场,协调 ClearingHouse 和 VAMM 之间的交互。本文将深入探讨 Exchange 的实现细节,包括其在系统中的作用、合约结构、多市场管理策略以及与其他组件的协作。
1. Exchange 在系统中的作用
Exchange 合约的主要职责包括:
- 管理多个交易市场(如 BTC/USD, ETH/USD 等)
- 为每个市场维护 VAMM 实例
- 处理市场参数的设置和调整
- 作为 ClearingHouse 和 VAMM 之间的中间层
Exchange 在系统中的位置:
2. Exchange.sol 合约剖析
市场数据结构
contract Exchange is IExchange, Ownable {
using SafeMath for uint256;
struct Market {
address amm; // VAMM 合约地址
address oracle; // 价格预言机地址
uint256 minRealizedPnlRatio; // 最小已实现盈亏比率
uint256 maxOpenInterest; // 最大未平仓合约数量
bool isMarketClosed; // 市场是否关闭
uint256 insuranceFundContributionRatio; // 保险基金贡献比率
}
mapping(address => Market) public markets;
address[] public marketList;
// ... 其他状态变量
}
核心函数
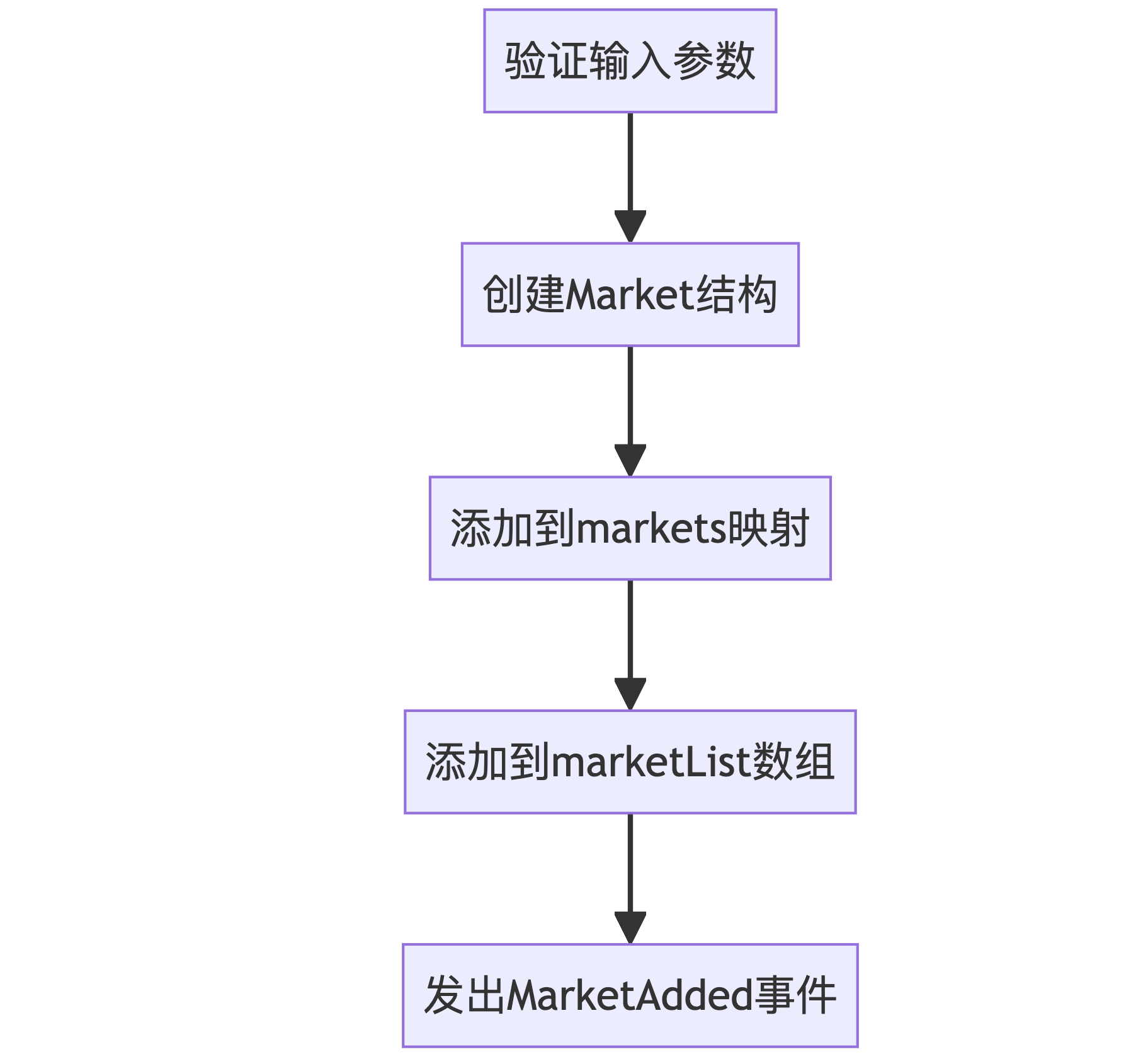
addMarket 函数
function addMarket(
address _amm,
address _oracle,
uint256 _minRealizedPnlRatio,
uint256 _maxOpenInterest,
uint256 _insuranceFundContributionRatio
) external onlyOwner {
require(_amm != address(0), "invalid amm address");
require(_oracle != address(0), "invalid oracle address");
require(markets[_amm].amm == address(0), "market already exists");
markets[_amm] = Market({
amm: _amm,
oracle: _oracle,
minRealizedPnlRatio: _minRealizedPnlRatio,
maxOpenInterest: _maxOpenInterest,
isMarketClosed: false,
insuranceFundContributionRatio: _insuranceFundContributionRatio
});
marketList.push(_amm);
emit MarketAdded(_amm, _oracle);
}
addMarket 函数流程:
removeMarket 函数
function removeMarket(address _amm) external onlyOwner {
require(markets[_amm].amm != address(0), "market does not exist");
require(markets[_amm].isMarketClosed, "market is not closed");
delete markets[_amm];
for (uint i = 0; i < marketList.length; i++) {
if (marketList[i] == _amm) {
marketList[i] = marketList[marketList.length - 1];
marketList.pop();
break;
}
}
emit MarketRemoved(_amm);
}
getMarketInfo 函数
function getMarketInfo(address _amm) external view override returns (Market memory) {
return markets[_amm];
}
3. 多市场管理策略
市场参数设置和调整
Exchange 合约允许管理员(通常是治理机制)调整市场参数:
function setMarketMinRealizedPnlRatio(address _amm, uint256 _minRealizedPnlRatio) external onlyOwner {
require(markets[_amm].amm != address(0), "market does not exist");
markets[_amm].minRealizedPnlRatio = _minRealizedPnlRatio;
emit MarketMinRealizedPnlRatioUpdated(_amm, _minRealizedPnlRatio);
}
function setMarketMaxOpenInterest(address _amm, uint256 _maxOpenInterest) external onlyOwner {
require(markets[_amm].amm != address(0), "market does not exist");
markets[_amm].maxOpenInterest = _maxOpenInterest;
emit MarketMaxOpenInterestUpdated(_amm, _maxOpenInterest);
}
// ... 其他参数调整函数
这些参数调整函数允许灵活地管理每个市场的风险和性能特征。
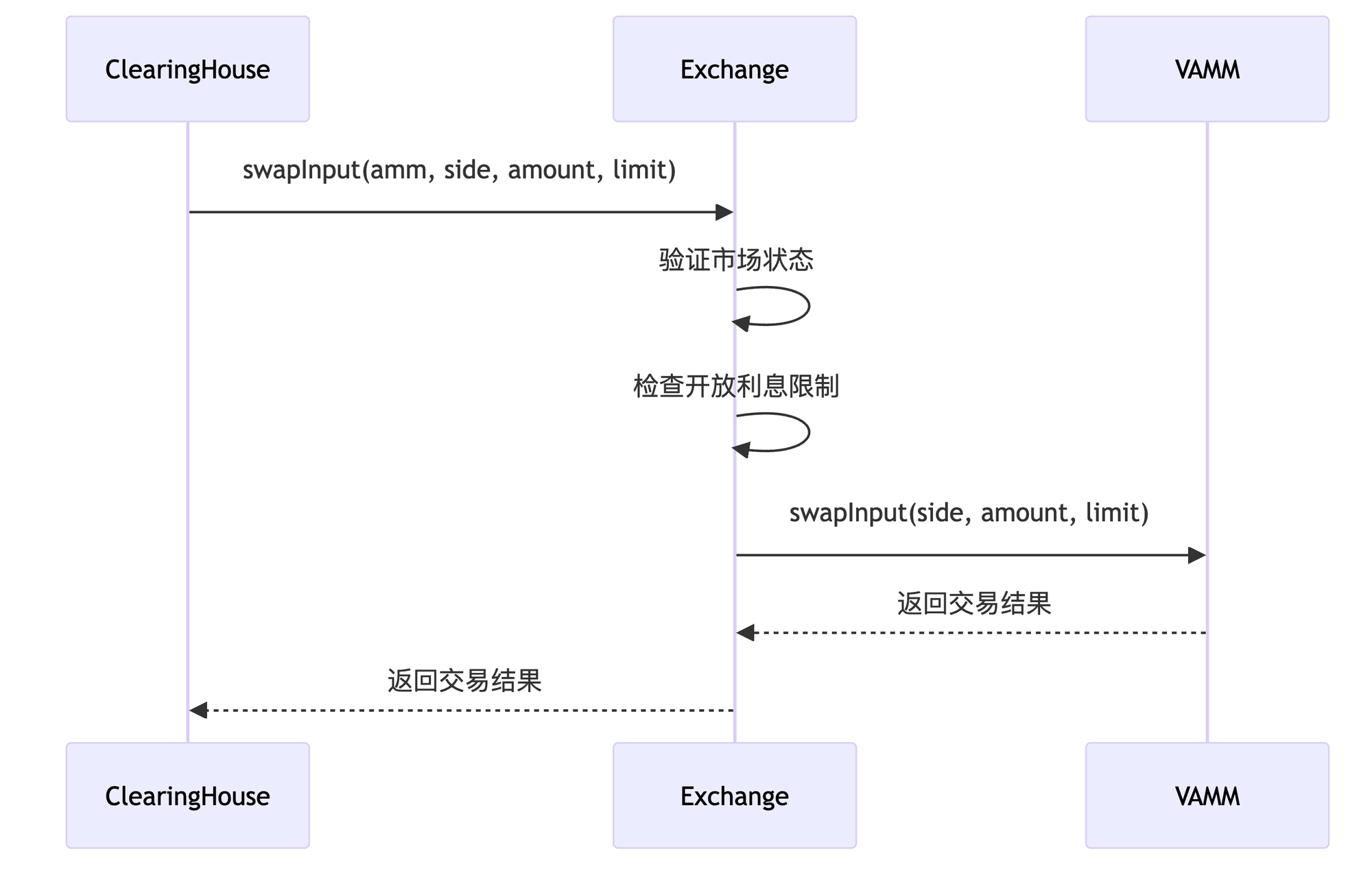
4. 与 ClearingHouse 和 VAMM 的协作
Exchange 作为 ClearingHouse 和 VAMM 之间的中间层,处理交易请求并转发给相应的 VAMM:
function swapInput(
address _amm,
IAmm.Side _side,
Decimal.decimal memory _quoteAssetAmount,
Decimal.decimal memory _baseAssetAmountLimit
) external override onlyExchange returns (Decimal.decimal memory, Decimal.decimal memory) {
Market storage market = markets[_amm];
require(market.amm != address(0), "market does not exist");
require(!market.isMarketClosed, "market is closed");
// 检查开放利息限制
checkOpenInterestLimitReached(_amm, _side, _quoteAssetAmount);
// 调用VAMM执行交易
return IAmm(market.amm).swapInput(_side, _quoteAssetAmount, _baseAssetAmountLimit);
}
与 ClearingHouse 和 VAMM 的协作流程:
总结
Exchange 合约作为 Perpetual Protocol 的核心组件之一,通过高效的多市场管理策略和灵活的参数调整机制,为整个系统提供了强大的可扩展性和适应性。它不仅简化了 ClearingHouse 和 VAMM 之间的交互,还为未来添加新的交易对和市场类型提供了便利。
通过深入理解 Exchange 的工作原理和实现细节,我们可以更好地把握去中心化衍生品交易平台的核心挑战和解决方案,为 DeFi 生态系统的进一步发展提供有价值的参考。
